Reducing inputs is a crucial part of today’s sustainable livestock farming systems. Able to supply up to 150 kg nitrogen/ha, white clover reduces the need for artificial fertiliser and the cost of application without impacting grass yield. This white clover seed guide will get you up to speed with how to effectively use this forage crop in your livestock farming system.
Research from Teagasc shows a potential 8% reduction in fertiliser use between now and 2030 through improved soil pH and increased clover in pasture swards.
A high-quality and digestible plant, white clover also supports higher animal feed intakes and enhanced performance. Research shows less fertiliser is required to produce the same amount of herbage from a clover/grass sward:

Germinal Horizon research shows clover can contribute significant levels of protein in a mixed sward, building across the season. It can also offer valuable metabolisable energy (ME), particularly when grass growth slows in the summer.
Metabolisable energy (ME) and crude protein (CP)
| Species | Early season | Mid-season | Late season | |||
| ME (MJ/kg) | CP (%) | ME (MJ/kg) | CP (%) | ME (MJ/kg) | CP (%) | |
| Perennial ryegrass | 11.73 | 14.46 | 10.84 | 12.82 | 11.03 | 15.64 |
| White clover | 12.21 | 32.81 | 11.21 | 24.46 | 11.54 | 26.67 |
White clover benefits
- Improves grazing quality
- Drives dry matter (DM) intake in summer and autumn
- Increases milk production and liveweight gain.
- Fixes atmospheric nitrogen making it available for plant growth.
- Lowers the need for N fertiliser application in summer.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process of clover fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere and making it available for plant growth. This nitrogen is available for uptake by white clover and other plants in the swards, particularly perennial ryegrass.
The amount of nitrogen fixed in a grass-clover sward depends on the following:
- White clover content of the sward: More nitrogen is fixed as clover content increases.
- Nitrogen fertiliser application rate: Less nitrogen is fixed if more artificial nitrogen is applied.
- Soil temperature: The rate of nitrogen fixation increases with a rise in soil temperature.
- Solar radiation (sunlight): More nitrogen is fixed on sunnier days.
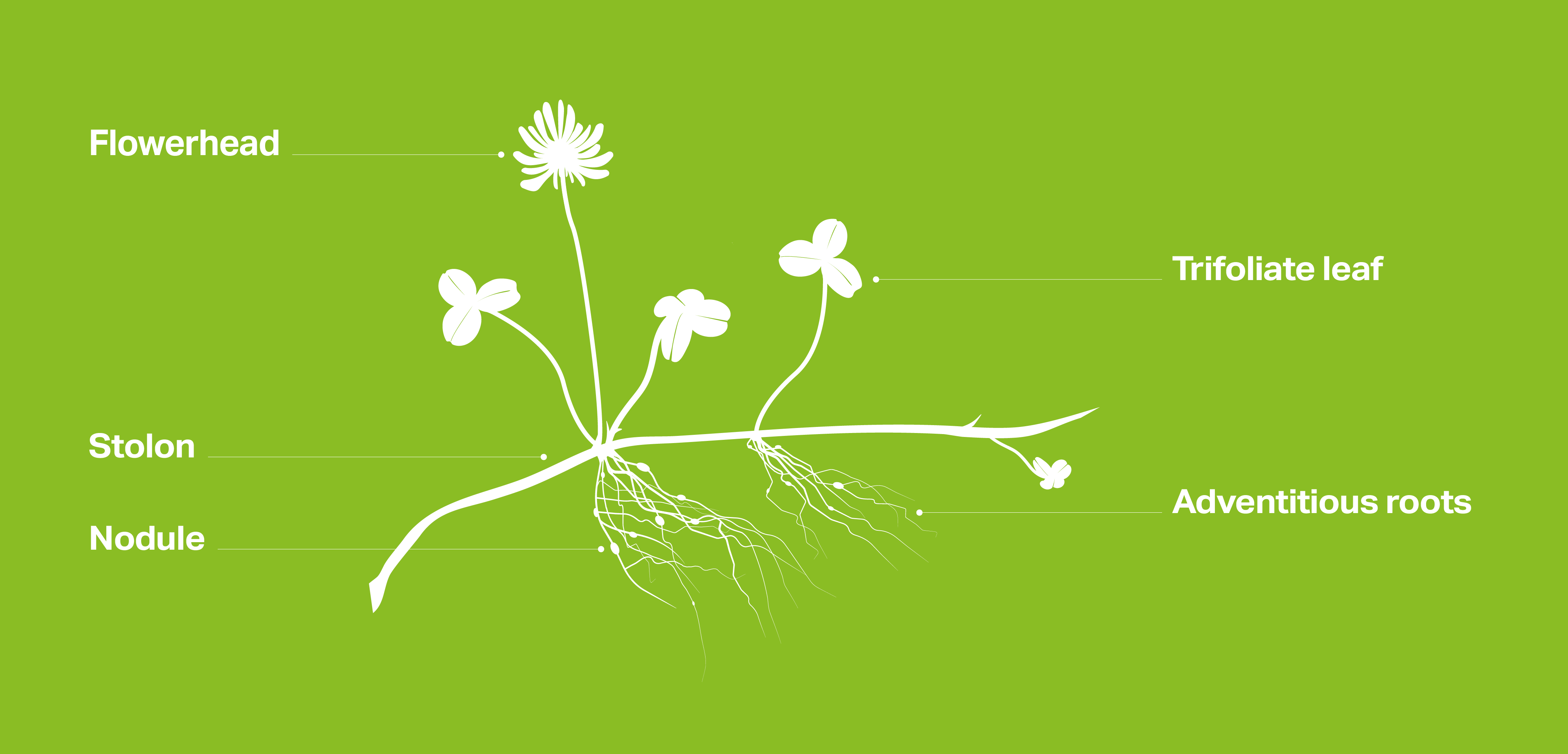
What are the white clover growth stages?
There are three white clover growth stages from germination to full establishment.
1. Rosette Phase
- Approximately 0-3 months post sowing
- Reliant on the central taproot
- Few branches
- Small spread
- No nitrogen fixation
- Important to graze to promote growth
2. Expansion phase
- 3-6 months post sowing
- Still reliant on the central taproot
- Rapid expansion of up to 15 branches, 25-30 cm in size.
- Initially rooting on the stolons is poor so careful grazing required to avoid damage.
3. Clonal phase
- Reliant on adventitious roots forming on the stolon nodes.
- Stolons last for 12-18 months with the cycle repeating each year.
- New stolons produced at the terminal bud producing independent plants.
- Good grazing management helps maintain stolon production and persistence in grazing swards.
- Active nitrogen fixation

How to sow white clover seed
Establishing white clover as part of a full reseed will give the best results in terms of clover content. It can, however, also be oversown into existing swards. Soil conditions must be right whichever method you use; this species likes fertile soil with a pH of 6.0 or above and Index 3 for P and K.
You can also consider combining white clover with red clover seed when establishing multi-species swards.
Full reseed:
- Sow 1-2 kg white clover seed per acre, with the higher rate necessary for good crop establishment
- Sow from May to early August
- Use a clover-safe spray for post-emergence weed control.
When to sow white clover seed?
Germinal recommends sowing from May until early August when soil temperatures are on your side. Any later and there's a risk of white clover failing to establish.
Derogation farms:
When reseeding, derogation farms must sow a minimum of 1 kg coated white clover seed or 0.6 kg uncoated seed per acre.
Germinal coated white clover seed
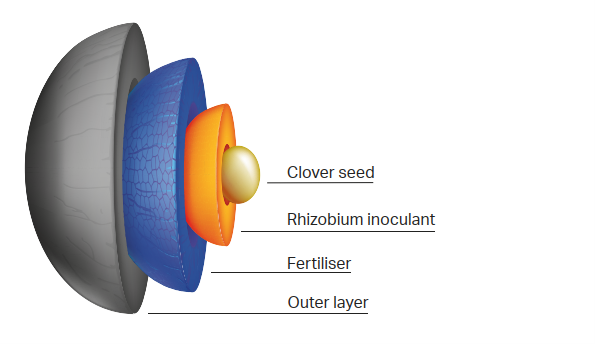
To gain the most benefit, an established sward needs a clover content of 25-30%. Clover is slower to establish than grass due to its smaller seed size, so Germinal’s white clover seed is coated to improve establishment and productivity. The larger seed size creates better soil-to-seed contact, and the coating contains beneficial ingredients to aid improved germination and provide more energy to the seed. These ingredients include:
- Fertiliser containing phosphorus to promote root growth and allow the clover plant to establish quicker and better compete with grasses for soil nutrients.
- Rhizobium inoculants to cause rapid nodulation by rhizobium strains which fix N for the clover and grass plants.
Coated white clover seed has been shown to establish quicker and produce seedlings with longer petioles and larger leaves. It can be used successfully in a full reseed or when overseeding clover into an existing sward. Whichever way it is used, managing it well improves the rate of establishment.
Coated white clover seed
Overseeding white clover
Sowing clover as part of a full reseed gives the best chance of success but if oversown into existing grass swards, there are several important points to remember:
- Start by controlling weeds, checking the herbicide residue period - it can
be up to four months before clover can be oversown safely - Take a silage cut or graze tightly and remove any grass thatch to give
good soil visibility and soil-to-seed contact - Use Germinal’s bigger and heavier coated clover seeds for better soil
contact - Oversow at 3-4kg coated clover/acre
- Don’t begin oversowing if dry weather is forecast – moisture is important
for germination
Using a fertiliser spreader:
Clover can be stitched in or broadcast. To sow with a fertiliser spreader, mix 3-4 kg coated white clover seed with 1 bag of 0:7:30 per acre. Add the clover to the spreader once in the field to avoid the seed settling at the bottom of the spreader and giving an uneven spread. Clover seed doesn’t throw as far as fertiliser so spread at half rate in two directions – up and down as well as across the field – and only do five acres at a time.
Post sowing:
- Start grazing oversown swards after about 10 days, at light covers of 900-1,100 kg DM/ha and down to a 4 cm residual. This allows light to reach the sward base while the clover is establishing.
- For the second grazing, graze again at a low cover of approximately 1,000 kg DM/ha
- Subsequently graze at 1,200-1,400 kg DM/ha and to a residual of 4 cm
- Reduce N fertiliser for two rotations to reduce grass growth
Clover grazing management
Spring
- Target early spring grazing to kickstart clover growth
- Avoid poaching/damaging swards
- Be flexible by using on/off grazing and graze wetter paddocks in drier weather
- Target post grazing sward height of 3.5 cm
Mid-season (April to July)
- Maintain a pre-grazing cover of 1,300-1,600 kg DM/ha and a pre-grazing height of 8-10 cm
- Target post-grazing sward height of 4 cm
- Reduce N fertiliser on swards with >25% clover
Autumn
- Extend rotation length to build grass cover from early to mid-August
- Close the farm in rotation from early October
- Target post grazing sward height of 3.5-4.0 cm on the final rotation
- Avoid poaching/damaging swards
- Be flexible by using on/off grazing
- Reduce N fertiliser on swards with >25% clover in August
- Close paddocks with a high clover content towards the end of the final rotation
White clover varieties
Small leaf
- More persistent
- Lower yielding
- Tolerant of tight grazing, e.g. sheep grazing
Recommended: AberAce, AberPearl
Medium leaf
- Intermediate for yield and persistency
- Suitable for dairy and beef cattle grazing
Recommended: AberHerald, AberSwan
Large leaf
- Higher yielding
- Aggressive and can dominate a sward
- Suitable for silage swards
Recommended: Alice
Clover fix
A blend of coated white clover seed that is particularly suited to overseeding.
Ask a clover expert
Please contact our technical experts if you have any questions about white clover seed.
